Gantry cranes play an essential role in lifting and moving heavy loads across a variety of industries, from manufacturing to shipping. These versatile machines come in different designs, each tailored for specific tasks. Whether you're looking for a crane to lift heavy materials in a construction zone or one that can handle large containers in a port, gantry cranes provide a solution that is both efficient and safe.
In this article, we'll explore the different types of gantry cranes, their features, and how they contribute to industrial operations. We'll also discuss key factors to consider when selecting a gantry crane and how they are used in various sectors.
What Is a Gantry Crane?
A gantry crane is a type of crane where the lifting mechanism is mounted on a structure that moves on rails. The crane's frame is typically made up of two supporting legs, allowing it to traverse a large area, making it ideal for heavy lifting in confined spaces or open environments.
These cranes are designed for moving heavy loads, such as containers, machinery, and raw materials, with precise control and stability. Gantry cranes can be found in various sizes and configurations, with each one serving a unique purpose depending on the task at hand.
Types of Gantry Cranes
1. Single Girder Gantry Cranes
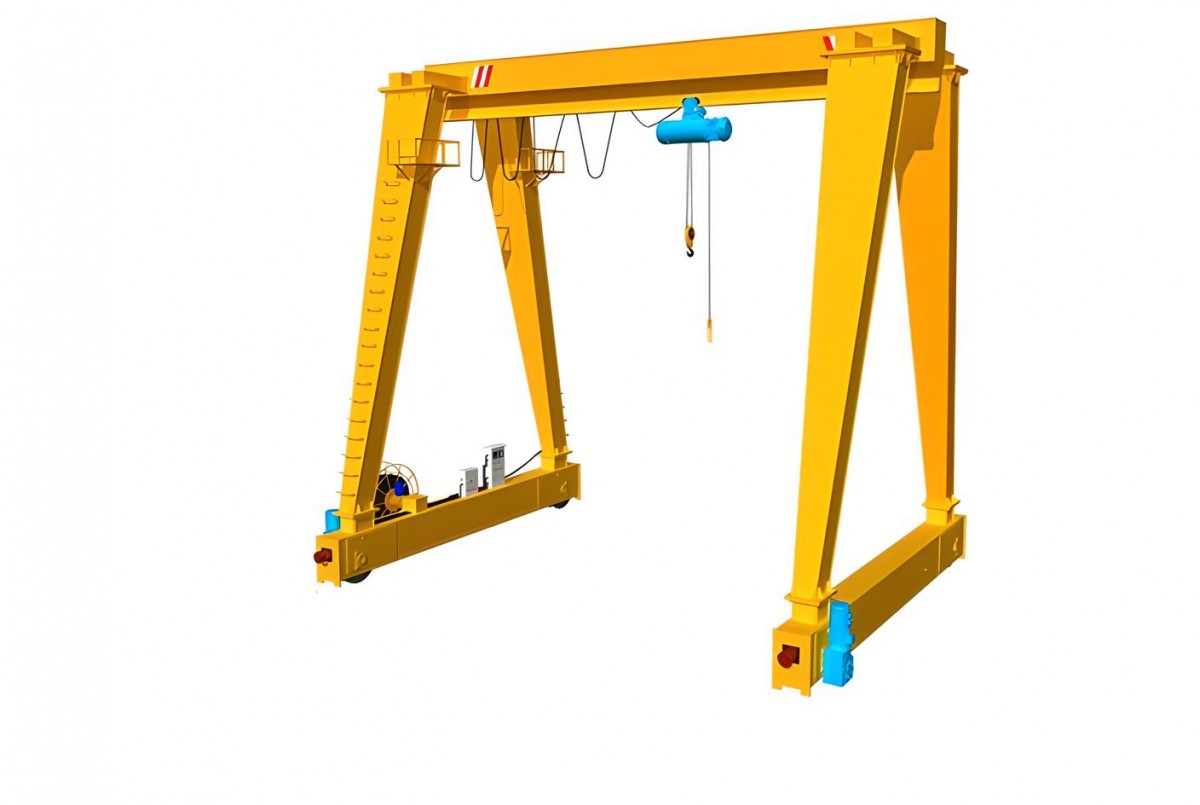

Single girder gantry cranes are one of the most common types used in smaller or less demanding applications. This type of crane has one main girder supported by two legs, which move along rails, allowing it to provide efficient and safe lifting capabilities for light to medium loads. Single girder gantry cranes are favored for their cost-effectiveness and compact design, making them ideal for operations where space is limited or budgets are tight.
With their single girder design, these cranes can lift moderate weights but generally have lower lifting capacities compared to their double girder counterparts. They are versatile and can be used in a variety of tasks, from moving smaller materials within a workshop to handling equipment in light manufacturing settings. Because of their simplicity, they are easy to install, operate, and maintain, making them an attractive option for businesses that don’t require heavy-duty lifting.
Industries that typically use single girder gantry cranes include warehouses, small factories, and maintenance facilities, where moderate lifting capacities are sufficient for day-to-day operations. These cranes are also used in sectors like automotive repair, where lifting heavy engines or car parts is necessary but does not require the massive lifting capacity of a double girder gantry crane.
2. Double Girder Gantry Cranes
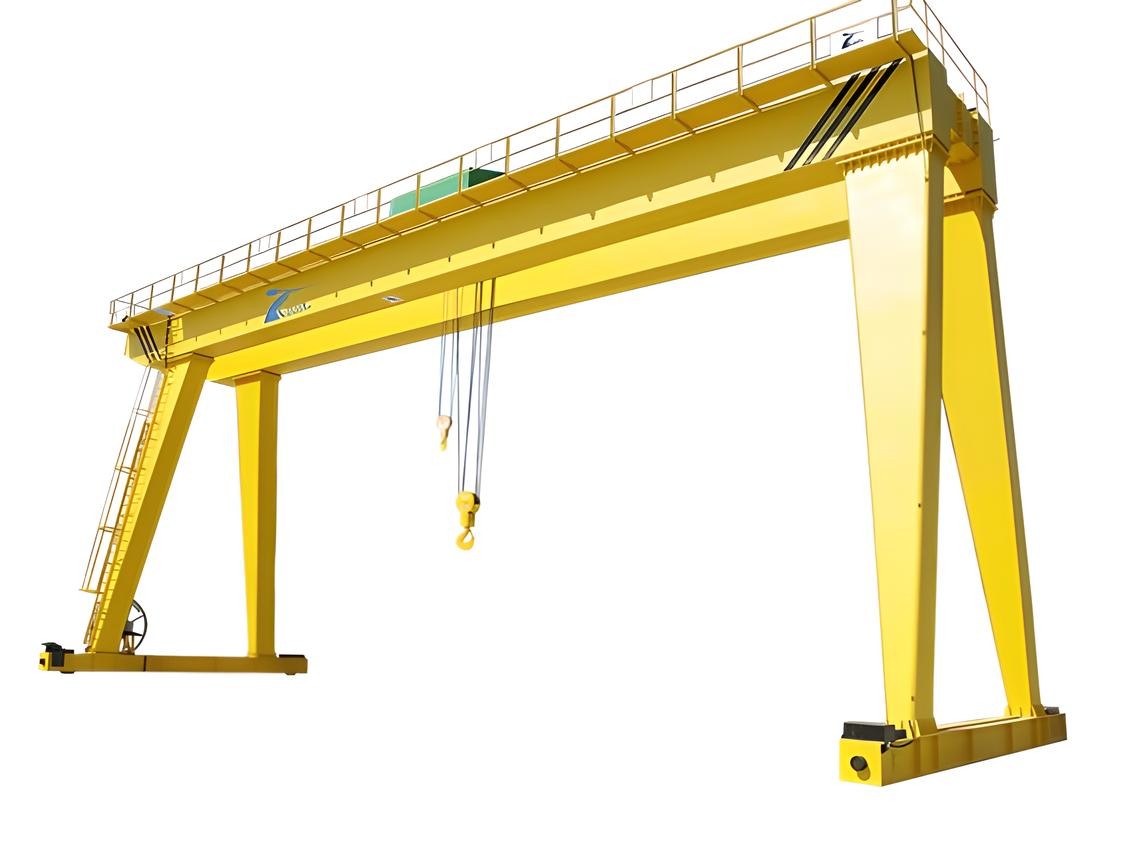

The double girder gantry crane is designed for heavy-duty tasks, with two parallel girders that provide added strength and stability. This type of crane is highly effective for lifting heavier loads and covering greater spans, which makes it an essential tool in large-scale operations. The double girder design allows for higher lifting capacities and increased durability compared to single girder cranes, making it ideal for demanding industrial tasks.
Double girder gantry cranes are particularly advantageous for handling very heavy equipment, large machinery, and bulky materials in environments that require high lifting capacities. The additional girder provides greater structural integrity, enabling these cranes to carry loads that exceed the limits of single girder models. They are equipped with powerful hoists and lifting mechanisms that allow them to move heavy materials efficiently and safely over long distances.
These cranes are commonly used in shipyards, steel mills, construction sites, and large warehouses. They play a key role in industries such as automotive manufacturing, construction, and heavy-duty equipment handling, where large components need to be lifted and transported across substantial distances.
3. Semi-Gantry Cranes
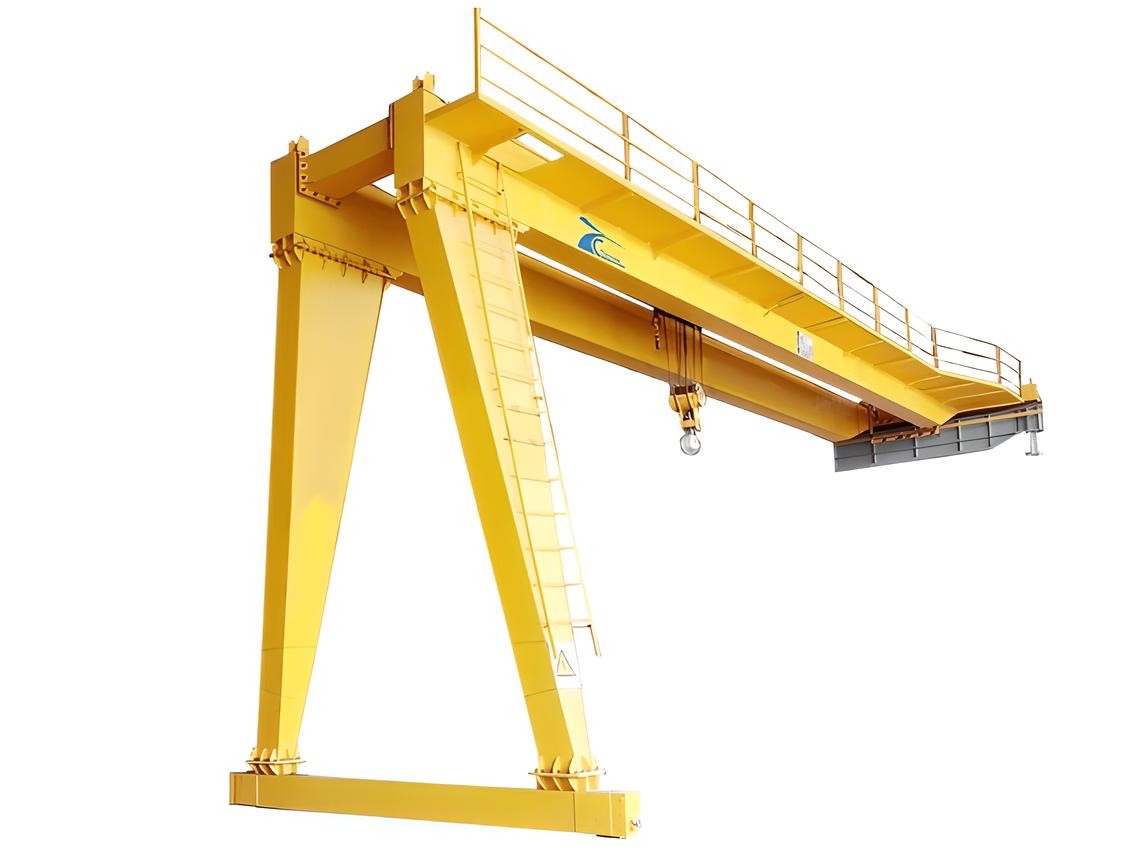

A semi-gantry crane is a hybrid model that combines aspects of both gantry and fixed cranes. In this design, one end of the crane is supported by rails or tracks, while the other end is fixed to a structure, such as a wall or building. This unique configuration provides flexibility and allows the crane to work in restricted spaces where a full gantry crane may not be practical or cost-effective.
Semi-gantry cranes are especially useful when there is limited space or when the crane needs to operate in a specific area without taking up valuable floor space. Because they can be partially fixed, semi-gantry cranes are also ideal for locations with a tight budget or smaller operational needs. These cranes offer a balance of portability and fixed positioning, allowing for efficient lifting and movement of materials in constrained environments.
Industries such as automotive manufacturing, construction, and maintenance workshops often rely on semi-gantry cranes for tasks that don’t require the full mobility of a gantry crane but still need the benefits of large lifting capacities. They can handle materials such as machinery, steel beams, and building components with precision.
4. Mobile Gantry Cranes
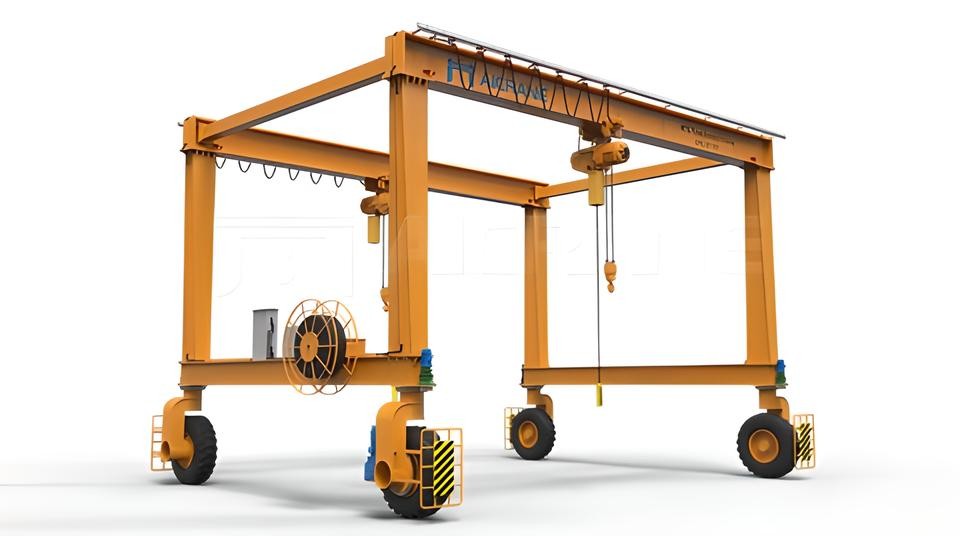

Mobile gantry cranes are versatile and portable, designed for industries that require flexibility in lifting and moving materials across different locations. These cranes feature wheels or casters that allow them to be easily moved from one point to another, making them ideal for operations that need equipment to be relocated quickly. Mobile gantry cranes are often used for lighter lifting tasks, but some models are designed for medium to heavy loads, depending on the application.
The key advantage of mobile gantry cranes is their portability. They are easy to assemble and disassemble, making them suitable for temporary setups or operations that require lifting at multiple points in a warehouse, construction site, or workshop. Mobile gantry cranes are commonly found in smaller-scale operations where flexibility is a must, as they can be adjusted to fit different work environments.
These cranes are used extensively in industries like automotive repair, construction, and small-scale manufacturing. They are also commonly found in maintenance operations, where heavy machinery or equipment needs to be lifted and moved in different locations within a facility.
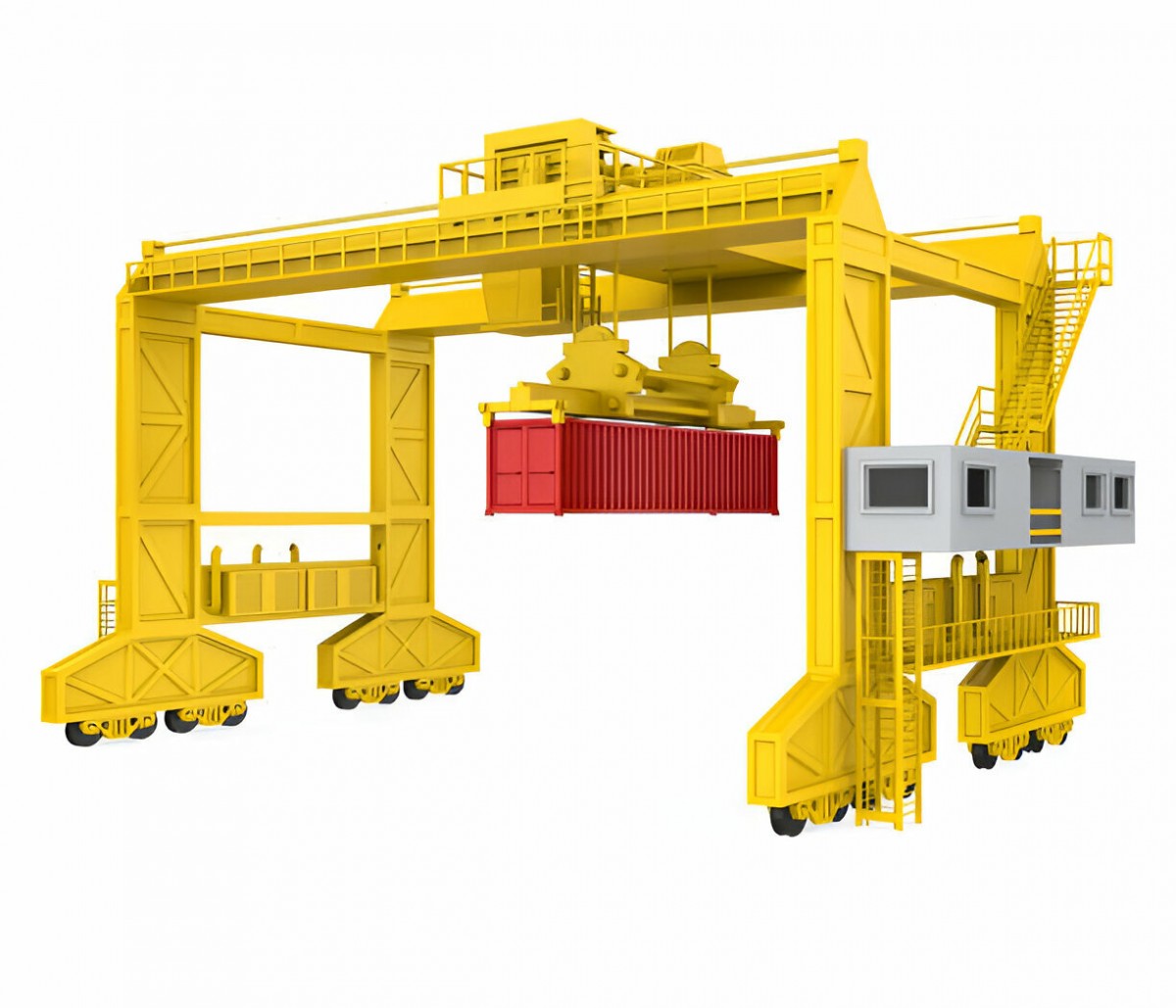
5. Container Gantry Cranes

Container gantry cranes are designed specifically for handling shipping containers, which are large, heavy, and often stacked in multiple tiers. These cranes are a staple in ports and logistics hubs, where they are used to efficiently load and unload containers from ships, trucks, and railcars. They feature robust hoisting mechanisms and can reach high above vessels to lift containers and place them on trucks or other storage areas with precision.
Container gantry cranes are designed to handle massive weights and provide high lifting capacities to accommodate the size and weight of shipping containers, typically ranging from 20 feet to 40 feet in length. These cranes can move large containers across long distances within the port, significantly speeding up operations and reducing turnaround time for ships.
They are primarily used in industries such as shipping, logistics, and international trade. Ports, container terminals, and logistics providers rely heavily on container gantry cranes for fast and safe container handling, playing a critical role in the global supply chain.
6. Shipyard Gantry Cranes
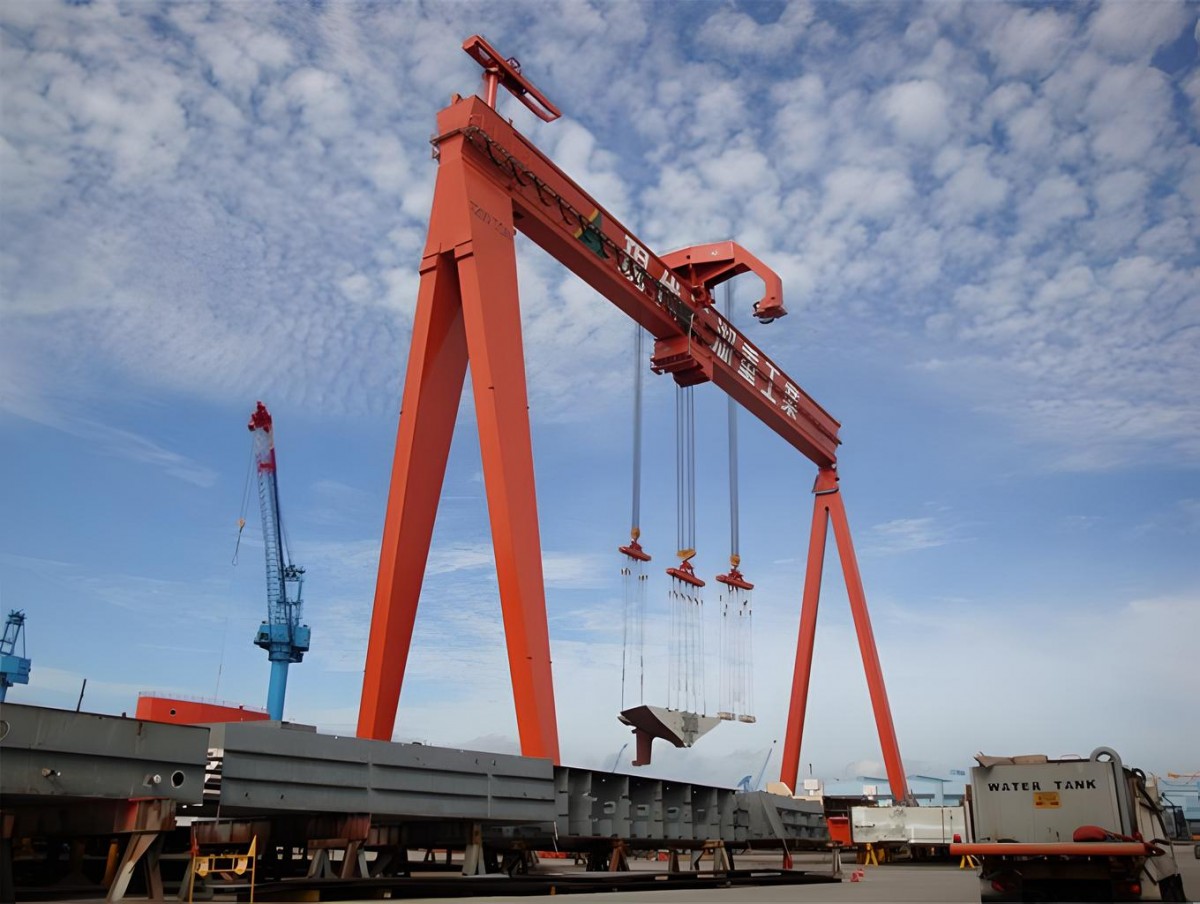

Shipyard gantry cranes are large, heavy-duty cranes specifically designed for use in shipbuilding and ship repair. These cranes are capable of lifting ships or large ship components, such as engines and hulls, weighing hundreds of tons. Shipyard gantry cranes are typically enormous in size, often spanning large dry docks or shipyards, and are equipped with powerful hoisting systems capable of handling extremely heavy loads.
Shipyard gantry cranes are used in the construction, repair, and maintenance of ships and maritime vessels, making them essential in the shipbuilding industry. They are designed for precise and safe lifting of ship parts, which can often be massive and difficult to maneuver without the assistance of a crane.
These cranes are used predominantly in the shipbuilding, ship repair, and maritime industries, where large vessels and ships need to be moved in and out of dry docks, as well as for lifting heavy ship parts for maintenance.
7. Portable Gantry Cranes
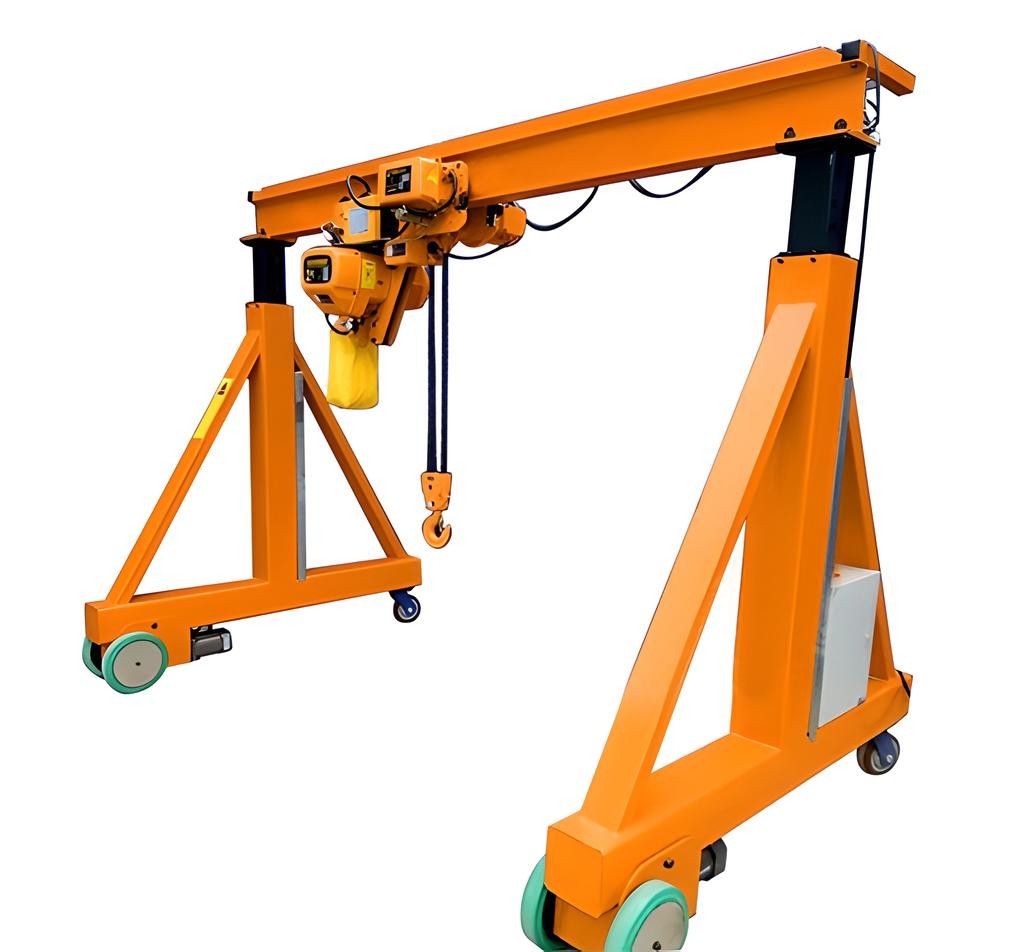

Portable gantry cranes are compact, lightweight cranes designed for easy transport and setup. These cranes are typically used for light to medium lifting tasks and are ideal for environments where space is limited or mobility is important. They can be easily assembled and disassembled, making them suitable for use in workshops, garages, and small-scale manufacturing facilities. Despite their smaller size, portable gantry cranes are sturdy enough to lift equipment such as engines, motors, or small machines with ease.
These cranes are a great option for temporary setups or locations where lifting needs change frequently. The portability and ease of use make them highly versatile, and they can be relocated quickly to different areas within a workshop or factory. Portable gantry cranes are ideal for maintenance teams, small manufacturers, and other industries where quick, efficient lifting is required without the need for a permanent crane installation.
8. Overhead Gantry Cranes
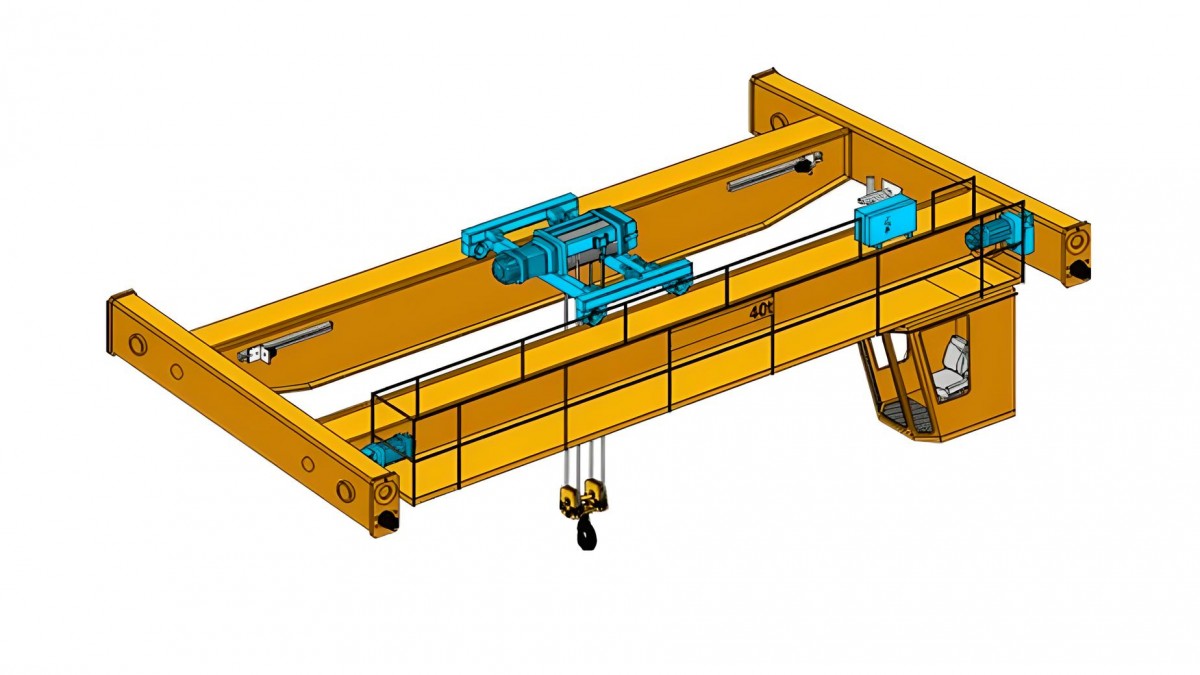
Overhead gantry cranes are similar to traditional overhead cranes but feature an additional set of supporting legs. These cranes span across a large area with two overhead beams, providing exceptional lifting flexibility. They are highly effective for handling large or heavy equipment and materials in large warehouses, manufacturing plants, and logistics centers. Overhead gantry cranes are ideal for heavy lifting and large-scale operations where significant spans and high lifting capacities are required.
Overhead gantry cranes are frequently found in heavy industrial operations, mining operations, and steel mills, where large and bulky items need to be lifted across expansive spaces. These cranes offer increased precision and capacity for moving large loads over long distances.
9. Adjustable Gantry Cranes
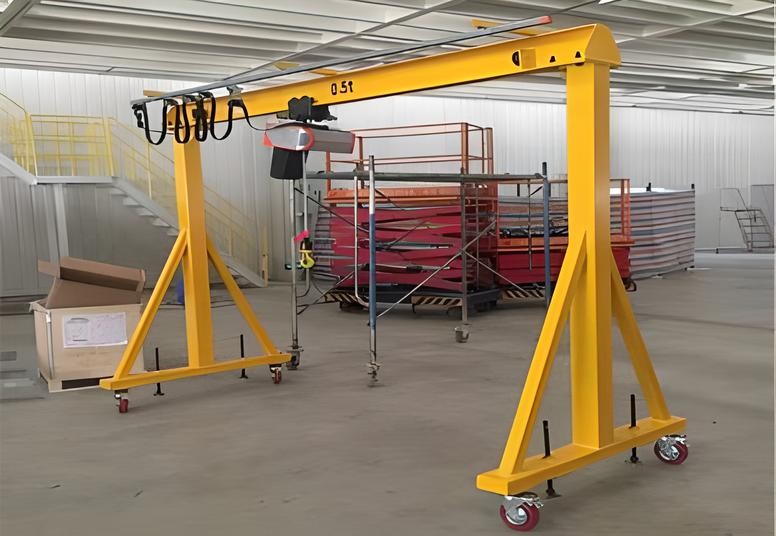

An adjustable gantry crane is a versatile lifting solution that allows for modifications to the crane’s height and span. This flexibility makes them suitable for handling materials of varying sizes and shapes. Adjustable gantry cranes are commonly used in environments where lifting needs vary from job to job, such as workshops, construction sites, or repair facilities.
These cranes can be configured to different heights and spans, providing flexibility for both small-scale lifting and larger operations. Adjustable gantry cranes are particularly useful in industries such as automotive, construction, and general manufacturing, where flexibility is essential for effective material handling.
10. Double Leg Gantry Cranes
Double leg gantry cranes are equipped with two sets of legs, which makes them ideal for large, heavy-duty lifting tasks. These cranes are particularly useful in environments where greater stability is needed, such as in shipyards and heavy construction sites. The two-leg design helps distribute the weight of the load more evenly, improving lifting capacity and safety during operation.
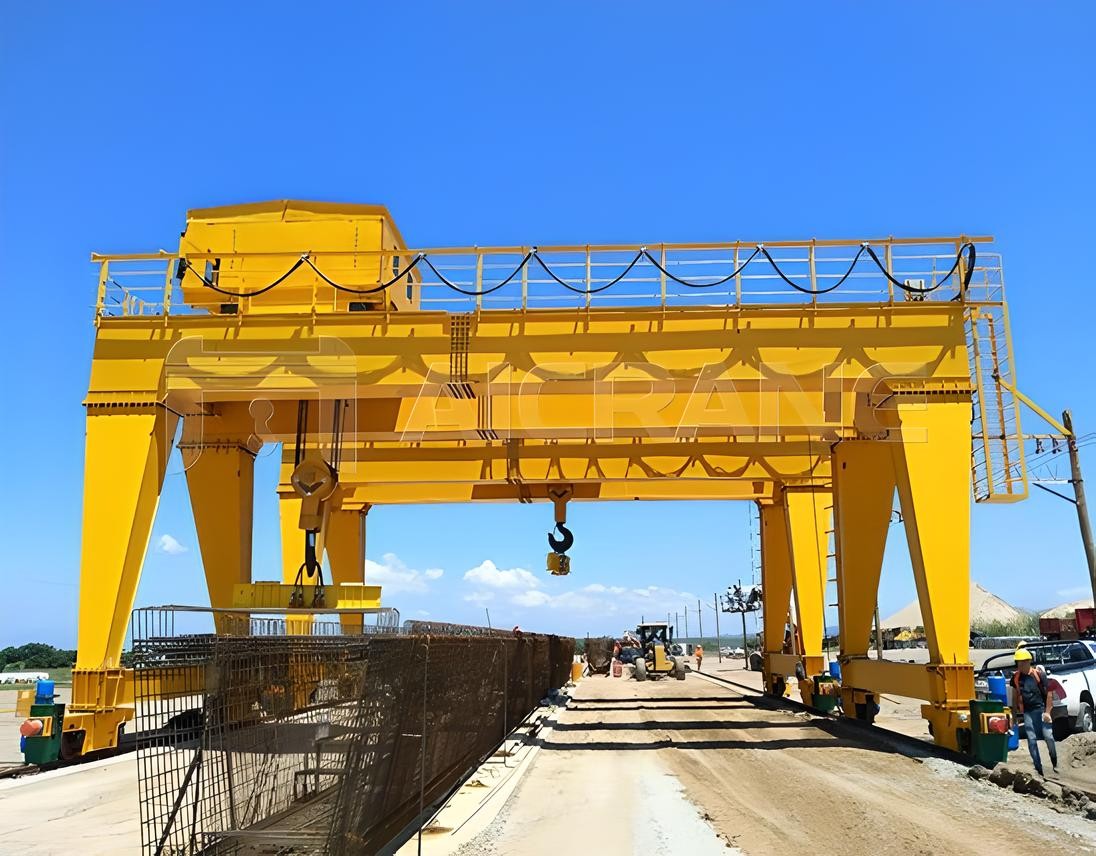

Image Credits: Aicrane
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Gantry Crane
When selecting a gantry crane, several factors should be considered to ensure the right crane for your needs:
- Load Capacity: Ensure the crane can handle the weight of the loads you intend to lift. Some gantry cranes are designed for lighter loads, while others can lift hundreds of tons.
- Span and Lift Height: Consider the distance over which the crane will be lifting and the height required for your operation.
- Space Availability: In tight spaces, a portable or semi-gantry crane may be ideal. Larger, fixed gantry cranes are better for expansive areas.
- Environment: Whether you need a crane for outdoor construction, a port, or an indoor workshop, choosing one suited for the environment is crucial. Some cranes are designed to withstand harsh weather conditions or work in confined indoor spaces.
- Mobility: If you need to move the crane between different locations, consider a mobile or portable gantry crane that can be easily relocated.
Applications of Gantry Cranes
- Construction: Lifting heavy building materials and machinery.
- Manufacturing: Moving components, machines, and large parts within factories.
- Shipping: Loading and unloading containers at ports and terminals.
- Shipbuilding: Lifting ships and heavy components during construction and repairs.
- Maintenance: Used for lifting large machinery and engines for maintenance or repairs.
1. What is the difference between a gantry crane and a jib crane?
A gantry crane typically consists of a bridge supported by two or more legs that move along tracks. It is used for lifting large and heavy loads over long distances. In contrast, a jib crane has a rotating arm (the jib) mounted on a fixed structure, and it is mainly used for lifting loads over short distances and within smaller workspaces.
2. How does a gantry crane work?
A gantry crane operates by moving along tracks or rails with its main bridge supported by two or more legs. The lifting mechanism (such as a hoist or winch) moves along the bridge to lift and lower heavy loads. The crane can move horizontally along the tracks and lift vertically, providing flexible movement of heavy items.
3. What industries use gantry cranes the most?
Gantry cranes are used extensively in industries like construction, manufacturing, shipping, shipbuilding, warehousing, and logistics. They are also used in ports, rail yards, and automotive industries for handling heavy machinery and materials.
4. What is the maximum weight a gantry crane can lift?
The maximum lifting capacity of a gantry crane can range from a few tons to more than 1,000 tons. For example, standard models in manufacturing might lift up to 20 tons, while specialized cranes like those used in shipyards or ports can lift up to 1,000 tons or more, depending on the specific crane design and purpose.
5. How do I choose the right gantry crane for my project?
Choosing the right gantry crane depends on factors like load capacity, span, height requirements, space availability, and whether the crane needs to be mobile or fixed. Consider the environment (indoor or outdoor) and the type of load (containers, machinery, etc.) to determine the best option for your needs.
6. What are the key features of a double girder gantry crane?
A double girder gantry crane has two main girders for added strength and stability, allowing it to lift heavier loads than a single girder crane. This type of crane is ideal for large-scale operations, and it provides higher lifting capacities, improved stability, and better durability for handling complex lifting tasks.
7. Can a gantry crane be used for lifting shipping containers?
Yes, gantry cranes are commonly used for lifting shipping containers at ports and logistics hubs. These cranes are specifically designed with specialized hoisting mechanisms to handle containers of various sizes (e.g., 20 ft, 40 ft) and are vital for containerized cargo operations.
8. What is the best gantry crane for a small workshop?
For a small workshop, a single girder gantry crane or a portable gantry crane would be ideal. These cranes are compact, lightweight, and cost-effective, providing enough lifting capacity for small tasks without taking up too much space.
9. How do you maintain a gantry crane?
Regular maintenance of a gantry crane includes inspecting the lifting mechanism, checking rail tracks for alignment, ensuring lubrication of moving parts, examining the electrical components, and testing the crane's safety features. It's crucial to follow the manufacturer's maintenance schedule and make repairs as needed to ensure safe and efficient operation.
10. What is the cost of installing a gantry crane?
The cost of installing a gantry crane can vary greatly based on its type, capacity, and installation location. Smaller portable cranes can cost a few thousand dollars, while larger, industrial gantry cranes (such as those for shipyards) can cost several hundred thousand dollars or more. Additional costs may include installation, maintenance, and operating expenses.
11. Can gantry cranes be used in outdoor construction?
Yes, gantry cranes are commonly used in outdoor construction projects, especially double girder gantry cranes and mobile cranes. They are designed to withstand the elements and are ideal for lifting large construction materials, steel beams, or equipment in open-air environments.
12. What is the difference between a semi-gantry crane and a full gantry crane?
A semi-gantry crane has one end mounted on a fixed structure or wall, with the other end mobile on tracks. This design is more space-efficient and cost-effective for specific tasks. A full gantry crane has both ends mobile, allowing it to operate across a larger area and lift heavier loads with greater flexibility.
13. How does the span of a gantry crane affect its performance?
The span of a gantry crane refers to the distance between the legs of the crane. A wider span allows the crane to cover more area and handle larger loads, while a narrower span may be suitable for more confined spaces. The span directly impacts the crane's lifting capacity and range of motion.
14. Are gantry cranes suitable for use in a port or logistics hub?
Yes, gantry cranes are essential in ports and logistics hubs for container handling. Container gantry cranes, in particular, are designed to efficiently load and unload shipping containers from vessels, trucks, or trains, making them a vital part of port operations.
15. How does a shipyard gantry crane handle large ships?
A shipyard gantry crane is specifically designed for lifting large ships or heavy ship components. These cranes can span a dry dock or shipyard and are equipped with heavy-duty hoisting systems to lift and move entire ships or large maritime equipment. Some of these cranes can lift weights exceeding 1,000 tons and are crucial in ship construction and maintenance.